The global population continues to rise, bringing significant challenges to global food security. It is predicted that the global population will reach 9.7 billion people by 2050, leading to an increase in food demand. However, the natural resources required for food production are depleting. To address this challenge, scientists and technologists have developed solutions to optimize food production and ensure the sustainable use of resources.
1. Circular Economy in Food Production
The circular economy is a sustainable development model that optimizes resource use and minimizes waste. In a circular system, by-products and waste from food production are not discarded but reused or transformed into valuable new products. This reduces pressure on natural resources and lessens the need for fresh raw materials.
A successful example of the circular economy is the treatment of whey, a liquid by-product from cheese production. Instead of causing environmental pollution, whey is now recycled into valuable nutritional products like whey protein or lactose, which are used in sports nutrition or infant formulas.
Additionally, other food industries such as meat and seafood processing are also utilizing by-products to create new food ingredients, from proteins in animal plasma to gelatin from fish skins and bones. These examples demonstrate the potential of sustainable resource use in food production.
    |
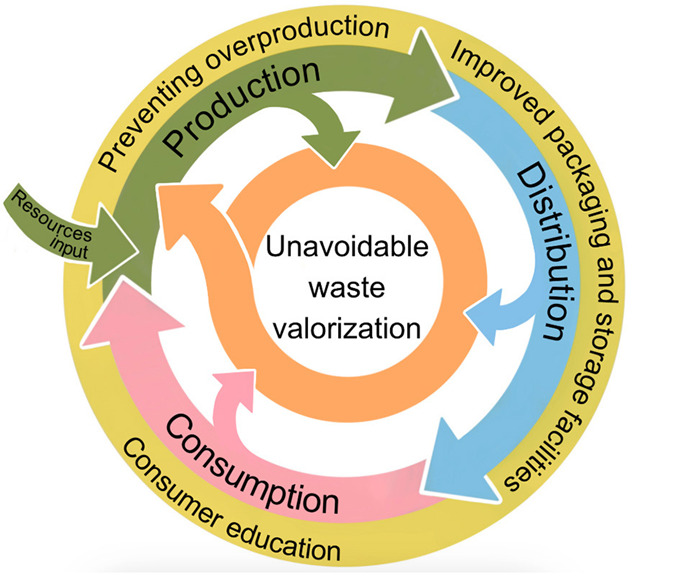 |
| Fig 1. Strategies to reduce food waste in the food supply chain in a circular food system: prevention for avoidable food waste (yellow curve) and valorization for unavoidable food waste (orange curve) |
2. Alternative Technologies and Sources for Food Production
In addition to adopting the circular economy model, new technologies and resources are being explored to meet the increasing global food demand. Some notable solutions include:
- Cellular Agriculture: This method of food production involves cultivating cells from animals or plants in a laboratory environment. For example, lab-grown meat can be produced without the need to raise animals, saving resources and reducing environmental impact. Cellular agriculture also allows for customization of the nutritional content of the product and the removal of unwanted elements like saturated fat or hormones.
- Insects: Insects are a rich source of protein and nutrients and are considered one of the sustainable solutions to global food needs. Although consumer hesitation remains, using insects in the form of protein powder or processed products may help increase market acceptance.
- Algae and Microalgae: Algae contain high levels of protein, fatty acids, and other beneficial nutrients. The use of algae in food production not only supplements nutrition but also reduces pressure on natural resources, as algae can grow in harsh environments without requiring land or freshwater.
3. Food Design and Digital Technology Application
Food design is a crucial aspect of creating new food products that not only meet nutritional needs but also make them more appealing and accessible to consumers. In particular, digital technology can play a key role in optimizing production processes and managing food supply chains.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can assist in predicting food demand, managing waste, and developing new food products. Technologies like Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) can enhance consumer experiences, encouraging them to adopt healthier food choices.
Moreover, blockchain technology provides traceability and transparency in the supply chain, ensuring food quality and boosting consumer confidence.
Conclusion
To ensure global food security in the coming decades, adopting the circular economy model and advanced technological solutions is essential. Methods such as cellular agriculture, using insects and algae in food production, and the support of digital technologies will help reduce pressure on natural resources while providing enough food for the growing population.
References
Valoppi, F., Agustin, M., Abik, F., Morais de Carvalho, D., Sithole, J., Bhattarai, M., ... & Mikkonen, K. S. (2021). Insight on current advances in food science and technology for feeding the world population. Frontiers in sustainable food systems, 5, 626227.